[ez-toc]
QuickBooks gives an error message reading “the file you specified cannot be opened” when unable to open a company file, such as when updating desktop software, performing payroll operations or opening federal or state forms.
Error 717 occurs due to either another program attempting to access it, or because its data has become corrupted and is no longer usable. There are various effective solutions available to remedy this issue, however.
Restart your computer
If your computer has frozen up and you are receiving an error that the file you specified cannot be opened, restarting could be the solution to help solve this problem quickly and easily. Rebooting should typically help resolve it quickly and effectively.
To restart your computer, press the F11 key on your keyboard. This will launch Windows Recovery Environment, allowing you to reset and restore normal operation of your machine. Following a reboot, try running any files that may have become inaccessible before.
Use Task Manager to stop any background processes using files you want to access. To do so, press CTRL+ALT+DEL and when Task Manager appears select all processes using those files then “End Process”. Repeat the same process for other files you are trying to gain access to.
Error message
When encountering this error message, one likely cause is that another program has access to the file you’re trying to open. But don’t assume this has to be true! In many instances, removing their permissions for using that file could help overcome this error message.
Another potential source of error could be that the file you wish to access has been blocked by another program; in such a situation, remove its permissions or check “Unblock”.
Alternately, you can run a disk check by running the Chkdsk utility. This program searches your hard drive for errors and helps to repair them; run this utility after experiencing problems or restarting PC. You should run it periodically as well.
Restarts depend heavily on the organization that opens a new school and its systems for smooth transitions and strong community support, as well as on any external organizations providing funding or technical assistance to ensure their success. Restart interventions have proven extremely successful when managed by high-performing organizations with schools properly prepared to thrive; as well as showing an association between restarts and higher student achievement rates.
Check for locked files
If you receive the error “These files cannot be opened” when trying to move or delete files on your computer, this is likely due to them being locked up and usually easy to fix.
Locking is a feature in Windows that prevents two programs from simultaneously editing the same file at the same time, to avoid conflicts that might affect other files on a system – especially on networked machines.
There are various kinds of locks in Windows; some can be advisory (when processes explicitly acquire a lock), while others must be mandatory (preventing reading/writing access to files by being locked out).
Locks are enforced by your operating system but can still be disabled if necessary. Some locking methods are so powerful they even lock whole disks to protect files from being altered without permission.
Sys Internals Process
Resource Monitor and Sys Internals Process Explorer are effective tools for detecting locked files. Both will display all processes using it at once.
Remember to close any processes using a file that are locking it to unlock it as this may often be easier than manually rebooting and emptying out its Windows Recycle Bin.
However, this option may not work in all instances and if you’re uncertain which files are causing these error messages then reaching out for assistance is best.
Unlocker is an alternative way of checking for locked files that is available for both Windows and Linux; download it here for free. Unlocker is a straightforward program that will identify which process is utilizing your file before providing you with options to unlock it and view its path and other details; unfortunately it does not provide an exhaustive list of processes which have secured or locked the file(s).
Run QuickBooks in safe mode
Error messages such as, “the file you specified cannot be opened” can be extremely irritating, often signaling there is something amiss with a company file. But this issue can often be solved with just a few easy steps.
One of the first steps you should take when encountering any error with QuickBooks is rebooting your computer, if this doesn’t help then running QuickBooks in safe mode may help as it limits installation of unnecessary drivers and apps that might otherwise exacerbate an existing error.
One important step you should take to protect the integrity of QuickBooks is ensuring your Windows operating system has been kept updated, which can protect against potential security vulnerabilities that could otherwise lead to issues when running QuickBooks.
If you are running an outdated version of QuickBooks, this could cause serious issues with both the operating system and other applications on your computer. To protect yourself, always check for updates for Windows to update to the most up-to-date release of QuickBooks.
potential errors
Once your operating system has been updated, it is advisable to run QuickBooks in safe mode in order to allow the software to identify and correct any potential errors that could be contributing to its malfunction. Doing this may allow it to identify and rectify any problems as soon as they arise.
As an extra precaution, you should check that QuickBooks has adequate permissions before using it. You can do this by right-clicking the shortcut or.exe file and choosing “Run as Administrator.”
Safe mode will limit the number of drivers installed on your system, which should help to identify any errors that are causing issues with QuickBooks and get you back to work faster. In addition, using safe mode can speed up your computer while also speeding it up so QuickBooks runs quicker. It may be wise to run chkdsk utility if there are any concerns with your hard drive to check for and fix errors as well.
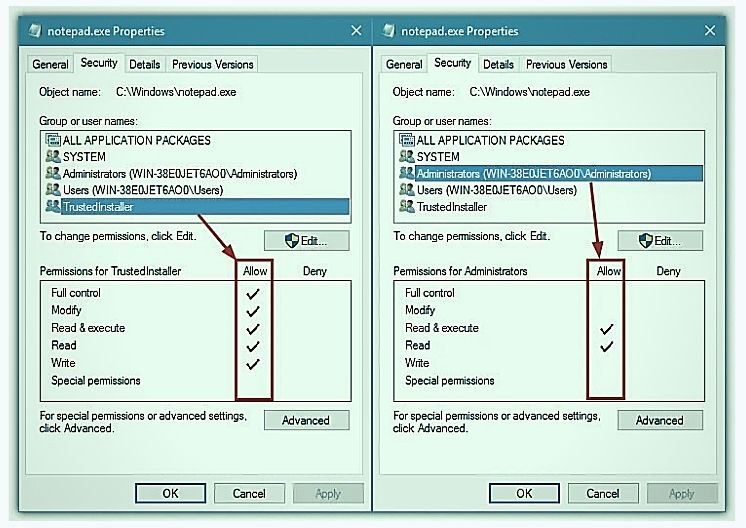
Check for permissions
Windows checks to see whether a file or folder belongs to an individual or group before granting you permission to view it. If it doesn’t, Windows verifies if you belong to one and whether that person or group has granted you the necessary rights before opening it for you. If neither scenario applies, Windows will investigate your membership in an appropriate group to see if you qualify to open it.
On Linux, each file and directory has a set of permissions that determine who can use it and for what purposes. These include both its owner’s permissions as well as any users granted access to it.
Permissions are indicated by a series of characters following a directory (d) slot; each represents a different category. For instance, user or owner permissions (r/w/x) correspond with user/owner read/write/execute capability while group permissions (g/o/) indicate group rights versus other users accessing it.
A dash in place of letters indicates that the category does not possess the permissions you are viewing. The number following the permissions represents either link count for files or directory entries contained.
Directories will appear
Mode column indicates how common data files and directories will appear; when dealing with other special files and directories it displays “d”.
These modes are important as they determine how the OS treats files or directories. For instance, if you create a directory which points directly to another directory then its mode will be “d”.
When you want to change the permissions of a file or directory as a user, using chgrp can help. This command lets you set permissions without changing its actual owner.
Other methods exist for changing permissions on files and directories, including setting suid and guid permissions – these methods may be less frequently employed but still prove helpful in certain instances.

